4Cs of Diamonds: All You Should Know
Oct 12, 2023
Simply put, the 4Cs of diamonds refer to Carat, Color, Clarity, and Cut. Established by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA), this standard has become the universal language of the diamond industry and the gold standard for quality.
The 4Cs of diamonds use a scientific and objective approach to reveal the unique characteristics of each diamond, providing buyers with clear and reliable reference points. Therefore, it is now widely recognized in the global diamond trade. In today's post, Darry Ring will delve into the specifics of the diamond four Cs and their grading criteria, helping you fully understand diamond quality assessment and make informed purchasing decisions.
CUT
Diamond cut in 4Cs refers to the proportional balance of table percentage, depth percentage, and symmetry obtained after a rough diamond has been cut and polished. It is an indicator used to assess the brilliance, fire, and sparkle of a diamond.
Although many mistakenly equate the diamond cut with the diamond shape, the two are entirely different. The diamond cut is essentially about the effect of the diamond's facets interacting with light, and it largely determines the diamond's shape.
Factors That Influence Cut
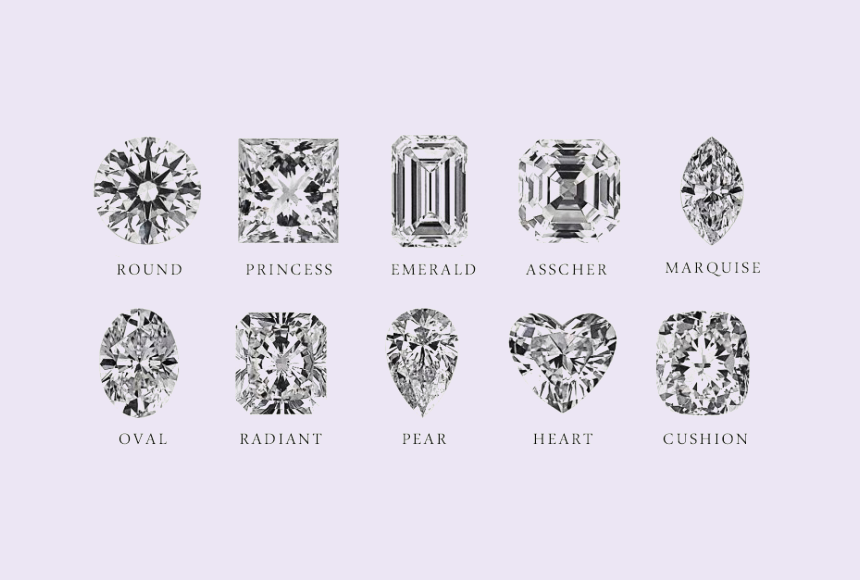
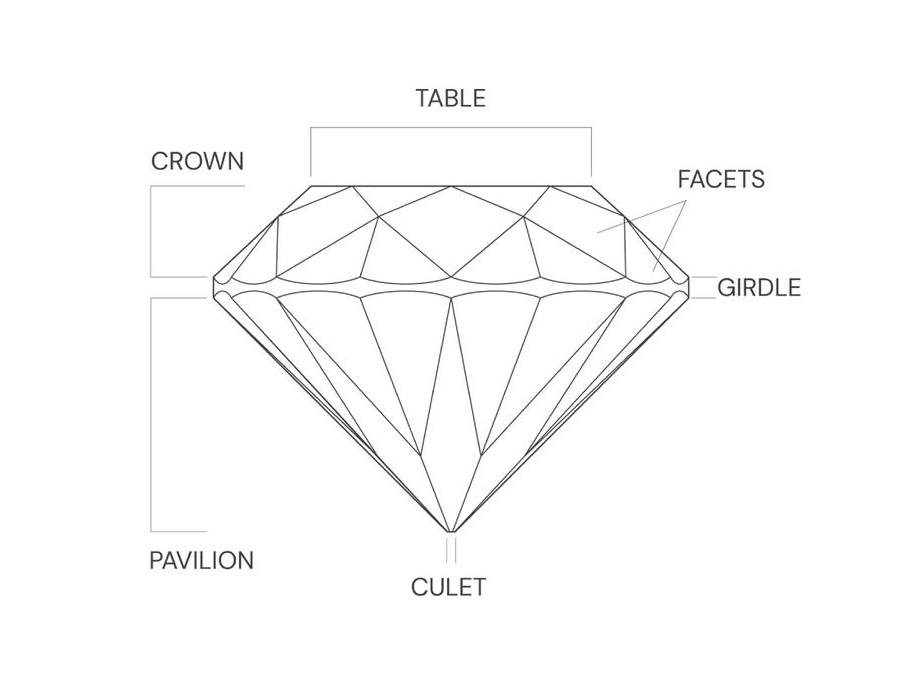
Conventional cut diamonds come in 10 common shapes, including round, pear, oval, marquise, and heart. But regardless of the shape, cut typically comprises 5 parts: crown, girdle, pavilion, and culet.
These parts of a cut diamond are closely linked to the final diamond quality. And the quality is determined based on table percentage, depth percentage, symmetry, and polish. Here is a breakdown:
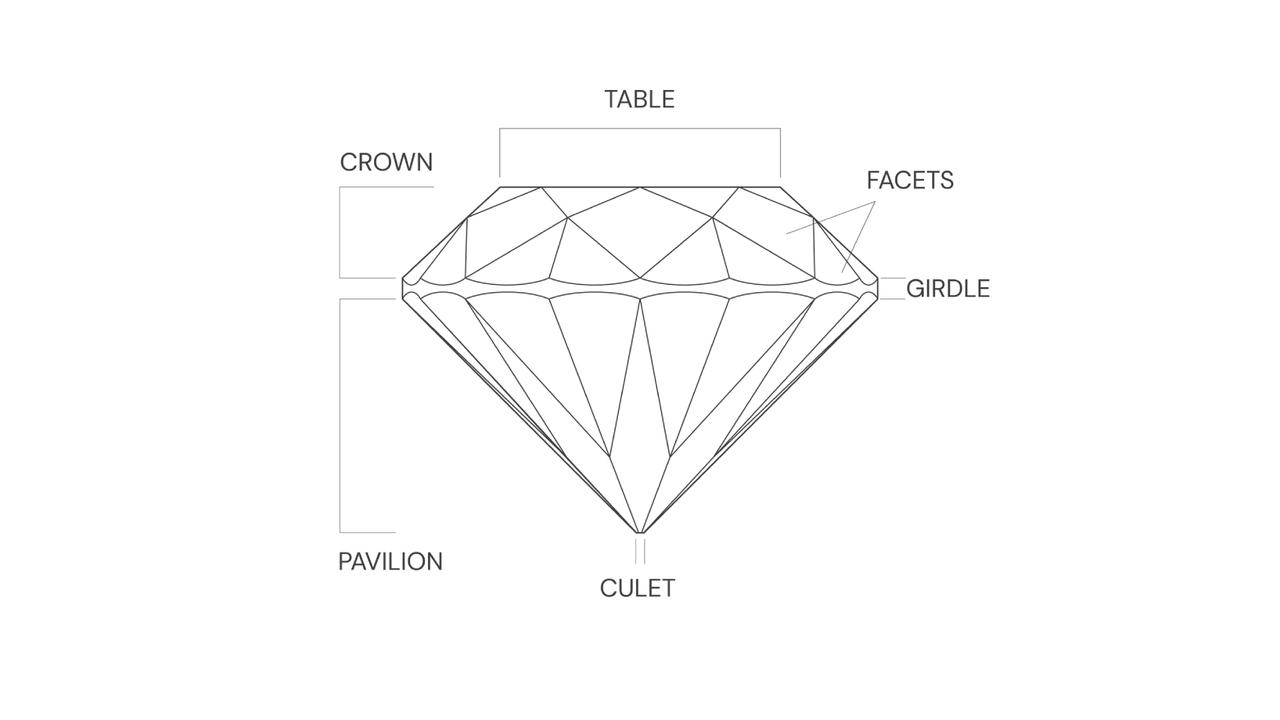
● Table Percentage refers to the ratio of the width of the diamond's top facets to its maximum width.
● Depth Percentage is the ratio of the height from the diamond's table to the culet, compared to the diamond's maximum width.
● Symmetry ensures that the facets surrounding the diamond are proportionally symmetrical, both in two dimensions and three dimensions.
● Polish refers to the smoothness and finish of each facet of the diamond after the cutting process.
The table and depth percentages are key factors in determining a diamond's brilliance and its ability to reflect light. The ideal proportions allow light to enter through the table, reflect off the pavilion, and exit through the table, creating maximum fire and brilliance.
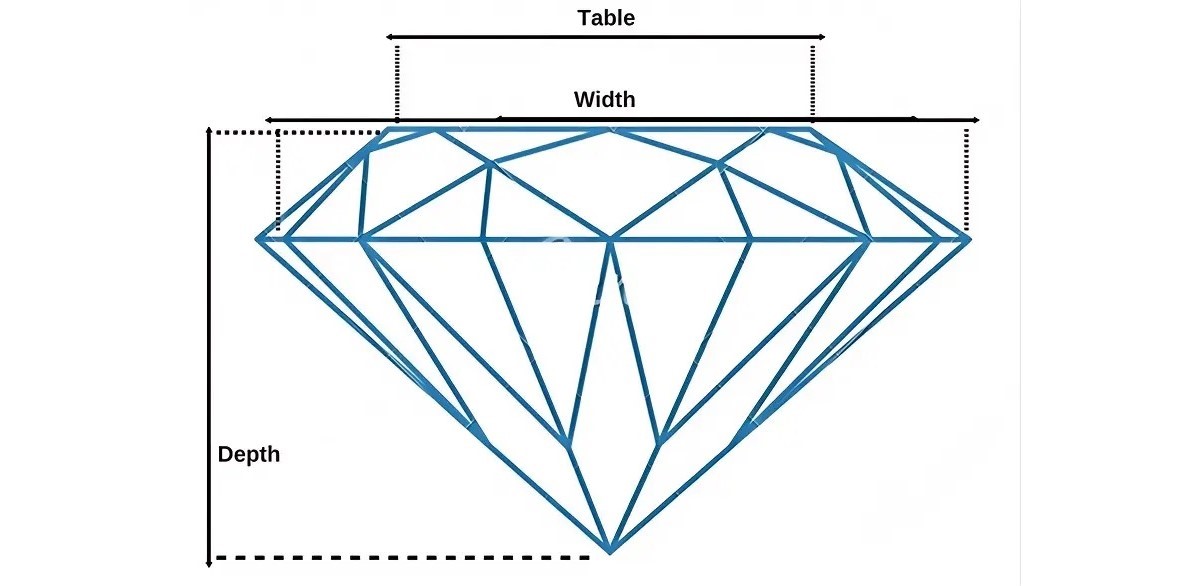
If the table percentage is too large or the depth percentage too shallow, light will escape from the diamond without reflecting back strongly. Conversely, if the table percentage is too small or the depth percentage too deep, light may become trapped inside the diamond or exit through the bottom, reducing its sparkle and fire.
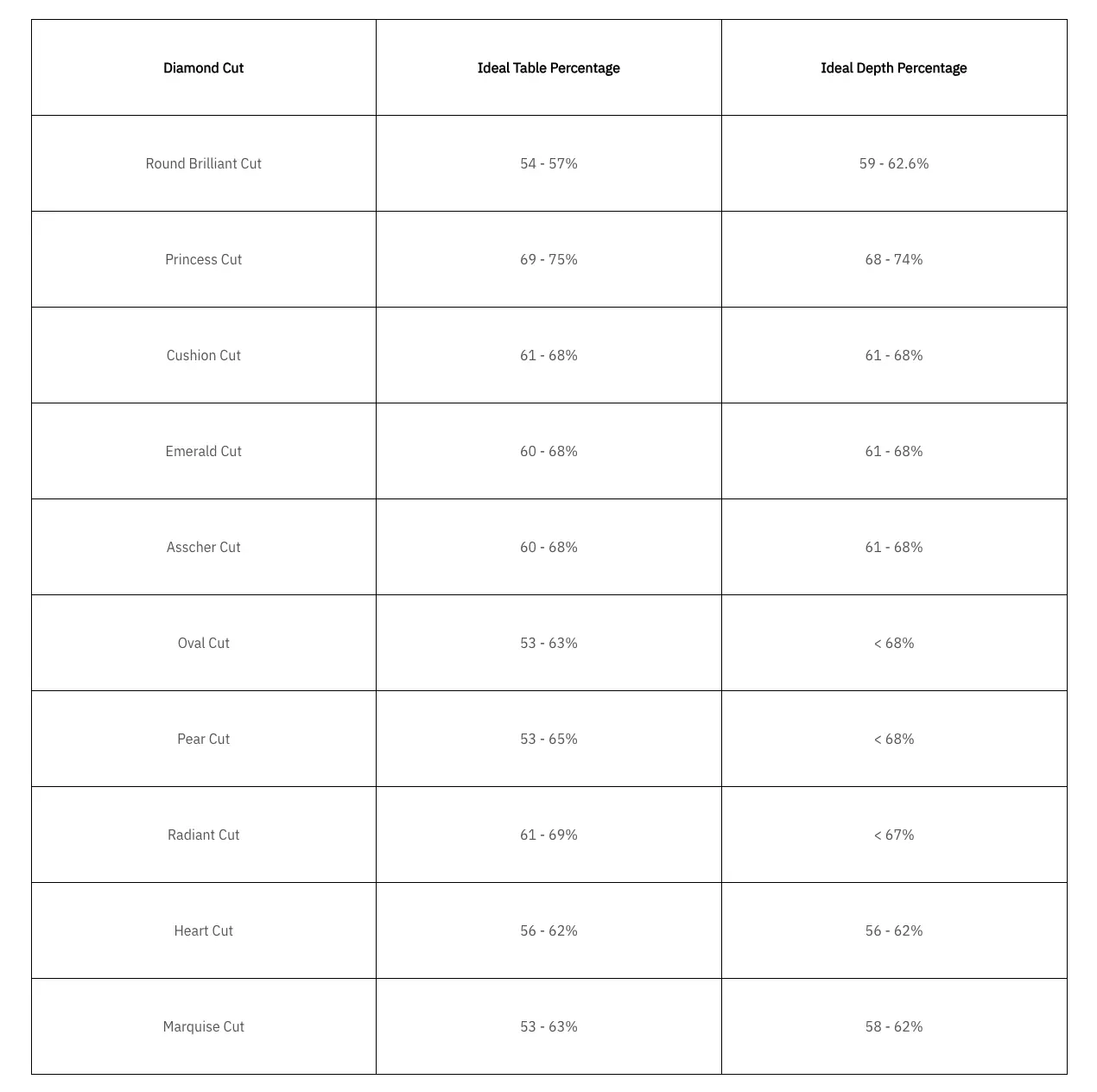
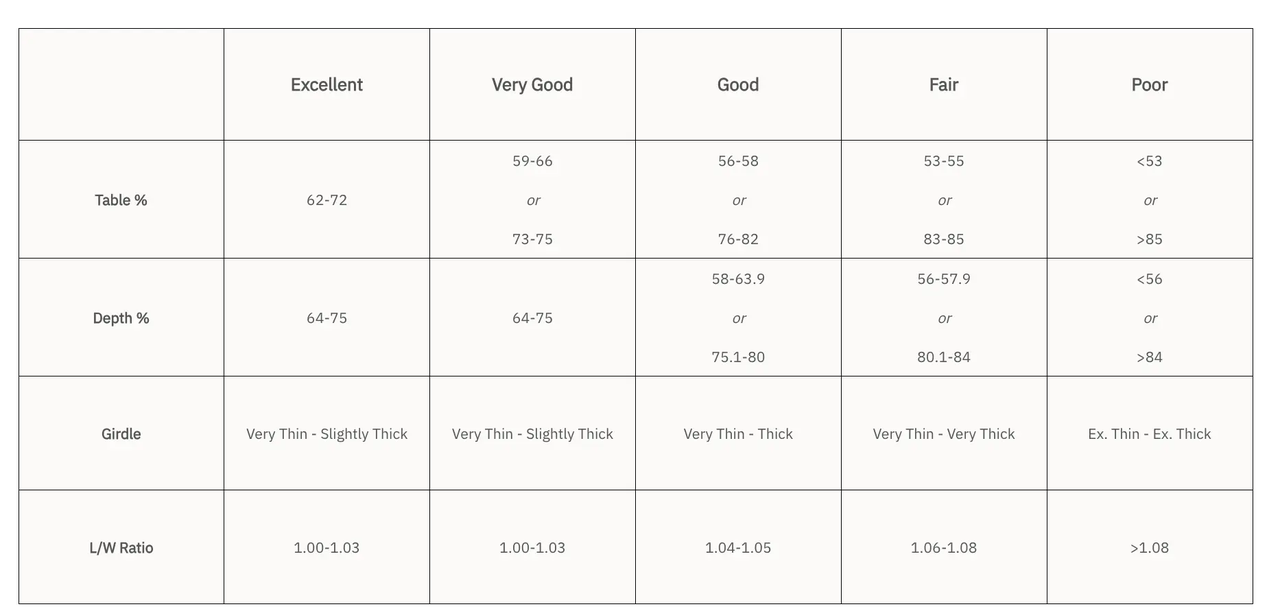
Therefore, depth and table percentage are two of the most important factors to keep in mind when referring to the 4Cs of diamonds and buying an engagement ring. Different diamond cuts have different requirements for the ideal diamond table percentage and depth percentage. Check out the right table for clearer details.
Diamond Cut Grade Chart
Of all the 4Cs of diamonds, the diamond cut grade is the most complex and technically challenging to analyze. It requires a comprehensive assessment of a diamond's brightness, fire, scintillation, symmetry, and polish. Based on different qualities, the GIA grades diamond cuts into five levels, from excellent to poor.
● Excellent: Diamonds with an excellent cut allow light to enter beautifully, resulting in high sparkle, brilliance, and a well-balanced pattern of light and dark areas.
● Very Good: Diamonds with a very good cut still exhibit strong sparkle and brilliance, but may have darker color near the edges or center.
● Good: Diamonds in this category have less sparkle and appear darker when light enters.
● Fair: Diamonds with a fair cut show only slight sparkle and brilliance when light enters.
● Poor: Diamonds in this grade are dull, with little to no sparkle or brilliance when light enters.
COLOR
The color of 4 Diamond Cs refers to the hue exhibited by the diamond. It is an indicator used to determine the subtle differences in color of a diamond from colorless to yellow. The Gemological Institute of America classifies diamonds by color starting from D (colorless) to Z (yellowish). The closer a diamond color is to colorless (D grade) the rarer the diamond (except for colored diamonds) and the higher the value.
Diamond Color Grade Scale
The GIA's specific diamond color grading, established in the 4Cs of diamonds, consists of seven levels. It is measured by comparing the diamond under controlled lighting and precise observation conditions to reference gemstones with a given color value.
● Colorless contains diamonds with color grades D - F. Colorless diamonds are the rarest on the market today and are usually set in platinum and white gold rings, making them the most valuable.
● Near Colorless contains diamonds with color grades G - J. The difference in color between these diamonds is so subtle that it is almost impossible for a layman to distinguish between them. Near-colorless diamonds do not exhibit significant color in most cases.
● Faint contains diamonds with color grades K - M. Starting from the color grade K, these diamonds can be seen by the naked eye to exhibit a faint yellow color. Due to the warm yellow hue of the metal, the faint yellow diamond can also be beautiful and delicate when paired with a yellow gold ring, which would be an affordable option.
● Very Light contains diamonds with color grades N - R. These diamonds are already fully visible to the naked eye with a very light yellow tint.
● Light contains diamonds with color grades S - Z. These diamonds can be seen with the naked eye as having a yellow or brown color.

CLARITY
In the 4Cs of diamonds, clarity refers to the presence of internal and external imperfections, known as inclusions and blemishes, respectively. These characteristics can affect a diamond's appearance and value. The fewer inclusions and flaws a diamond has, the higher its clarity and, accordingly, the higher its price.
Diamond Clarity Grade Chart
Diamond experts from organizations such as the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) and the American Gem Society (AGS) use microscopes with magnifications of 10x or higher to detect any inclusions and flaws present in a diamond. Based on their findings, experts assign a clarity grade to each diamond within a standard scale. This scale, or clarity grade chart, consists of six categories and 11 grades, ranging from Flawless to Included, as follows:
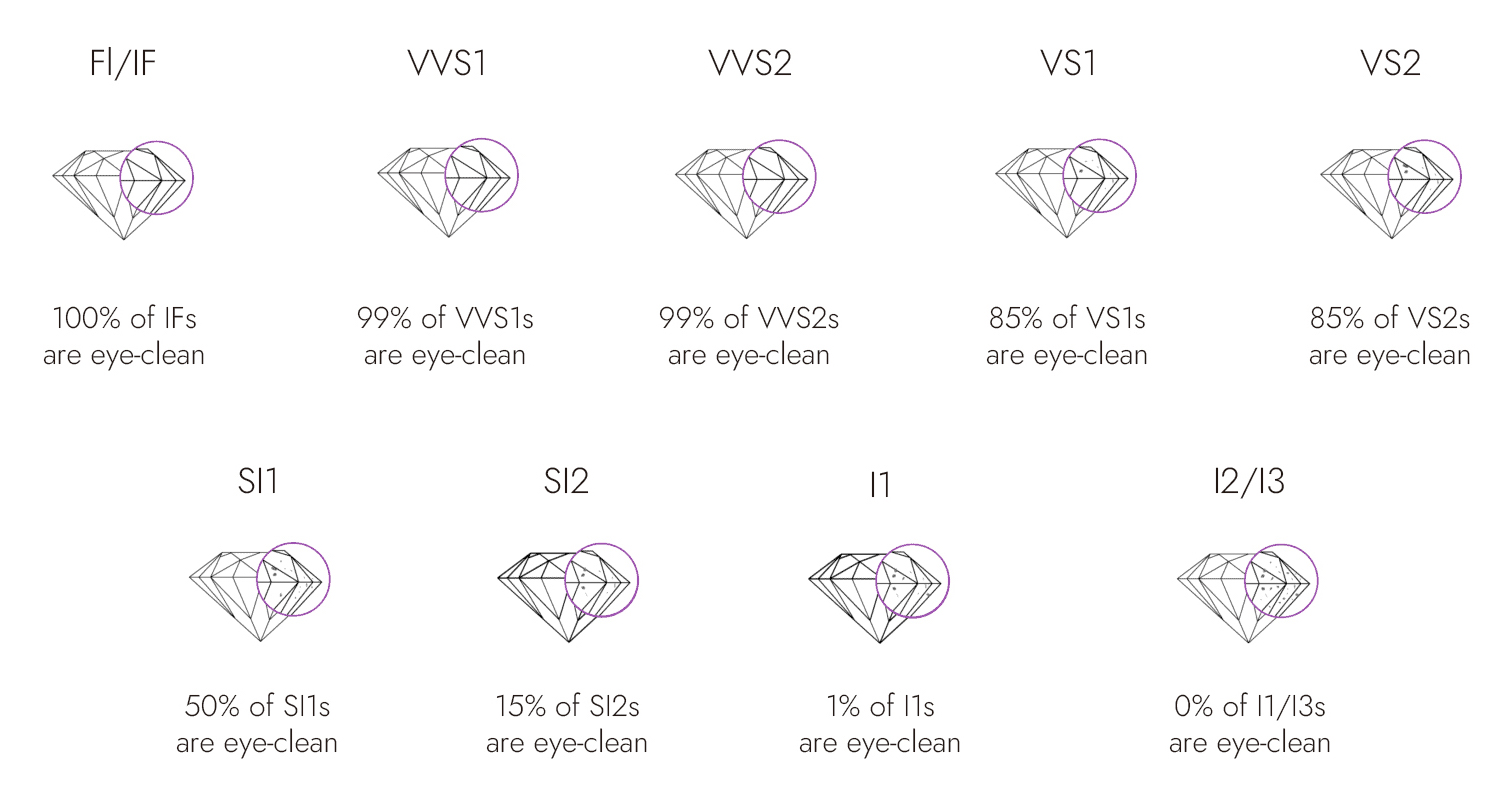
● Flawless contains diamond clarity grades FL (flawless) and IF (Internally Flawless). It means that the diamond is free of inclusions and flaws when viewed under 10x magnification. Flawless diamonds are the rarest diamonds.
● Very, Very Slightly Included contains diamond clarity grades VVS1 and VVS2. The inclusions in these diamonds are so slight when viewed under 10x magnification that they are difficult to see, even for a skilled grader.
● Very Slightly Included contains diamond clarity grades VS1 and VS2. The inclusions can be seen inside these diamonds when viewed diligently under 10x magnification.
● Slightly Included contains diamond clarity grades SI1 and SI2. The inclusions can be seen inside the diamond under 10x magnification. For emeralds and Asscher cut diamonds with grade SI2, inclusions are likely to be visible to the naked eye.
● Included contains diamond clarity grades I1, I2 and I3. The inclusions are obvious and clearly visible under 10x magnification. Most brilliant cut diamonds with clarity grades I2 and I3 have inclusions visible to the naked eye, which may have a significant impact on the fire and brilliance of the diamond.
CARAT
Carat in Four Diamond Cs refers to the unit of measuring the weight of a diamond. According to the GIA, one carat in the metric system is equivalent to 200 milligrams or 0.2 grams. Each carat can be subdivided into 100 "points", which is used by many jewelry businesses to describe the weight of a diamond under one carat. For example, a 0.25 ct diamond can be described as 25 points.
Diamond Carat Weight Chart
When people are looking at your diamond ring, most of their eyes are drawn to the diamond set in the ring. Although the carat in 4Cs of diamonds is not a unit of measurement for diamond size, as the carat weight of a diamond gets larger, the physical size of the diamond gets larger. As an example of a round cut diamond, view the sizes of diamonds of different carat weights in the table below.

How Big is a One Carat Diamond
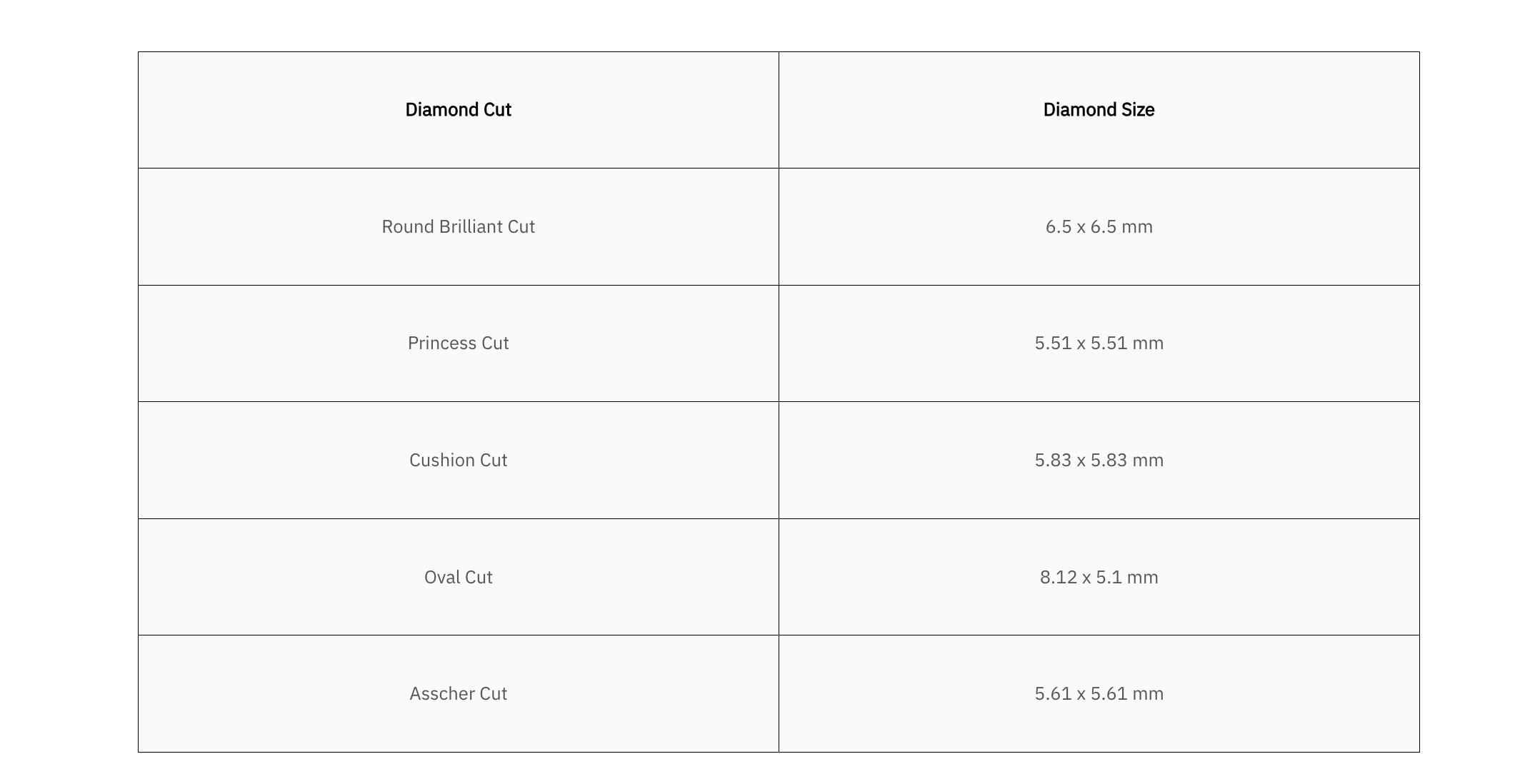
The size of a 1-carat diamond has a lot to do with the depth and shape of the diamond cut. If you compare 1-carat round diamond engagement rings with different depths of cut, you will notice that a deeper-cut round brilliant diamond will look smaller than a shallower-cut round diamond.
Different diamond cuts can also give a different impression for the same carat weight. For example, a one carat round brilliant diamond is approximately 6.5 mm in diameter, while a 1ct square brilliant diamond is approximately 5.61 mm in diameter. When viewed from the front, a 1ct round diamond engagement ring is much larger than a square diamond engagement ring. View sizes for different diamond shapes with the same 1-carat weight in the table below.
FAQs About 4Cs of Diamonds
Which C is most important in the Four Cs?
Among the 4Cs of diamonds, Cut is often considered the most important factor. Cut directly impacts a diamond's brilliance, fire, and sparkle. Even if a diamond has excellent color, clarity, and weight, it will lack the desired radiance and beauty if the cut is poor.
What are the 5Cs of diamonds?
The 5Cs of diamonds are an extension of the traditional 4Cs (Cut, Color, Clarity, and Carat Weight), with the addition of Certification, also known as Confidence. This "C" highlights the importance of authoritative diamond reports, assuring buyers that the diamond meets their expectations and giving them confidence in their purchase.
Related Articles
A Full Guide to 10 Common Diamond Ring Shapes
 15624 / Sep 25, 2023
15624 / Sep 25, 2023The 10 common diamond shapes include round, oval, marquise, pear, princess cut, cushion cut, emerald, radiant, asscher and heart. Click to learn more.
Learn More >
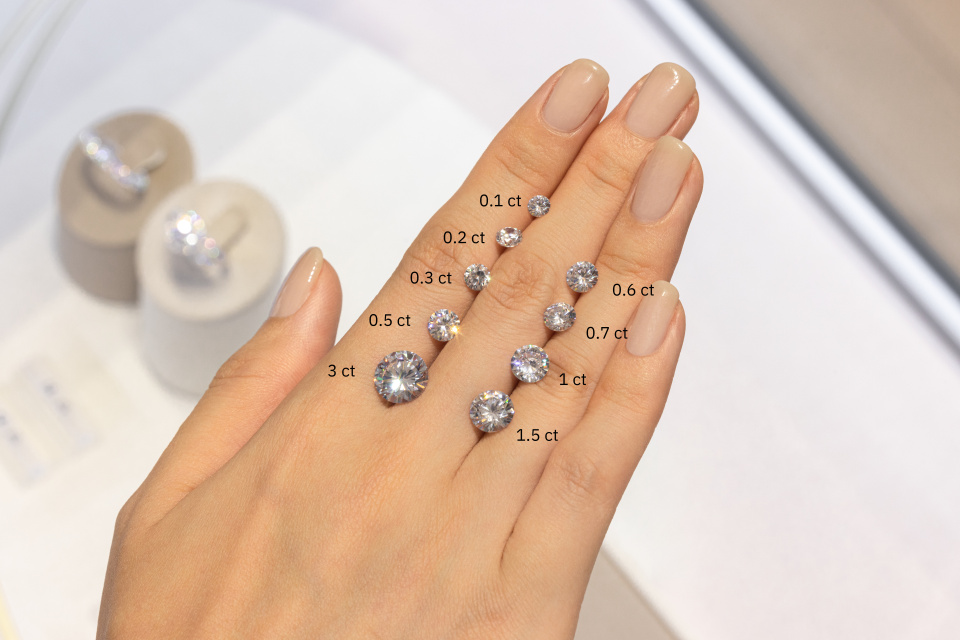

How Big is a 1 Carat Diamond? Detailed Answers
 22661 / Sep 25, 2023
22661 / Sep 25, 2023The size of a 1 carat diamond engagement ring is related to the diamond cut, shape and finger size, click to learn more how big is a 1 carat diamond.
Learn More >
What is A Diamond Cut?
 10973 / Sep 26, 2023
10973 / Sep 26, 2023Diamond cut isn't diamond shape, but the polish and symmetry, table and depth percentage of diamonds to assess quality. Click for top 5 DR engagement ring cuts.
Learn More >